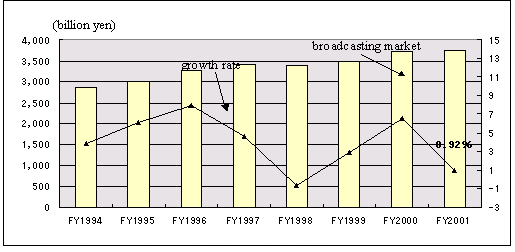
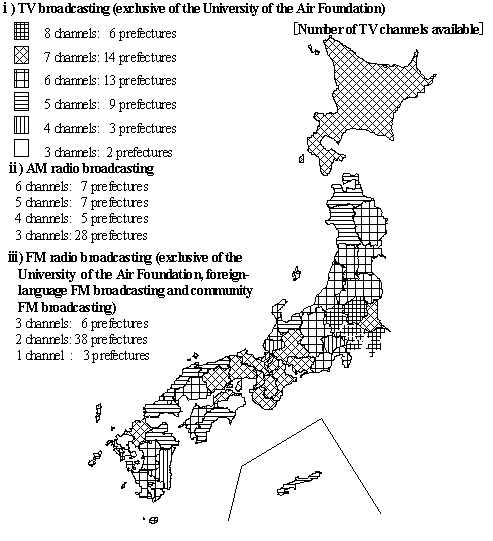
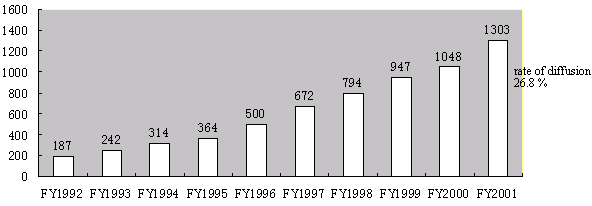
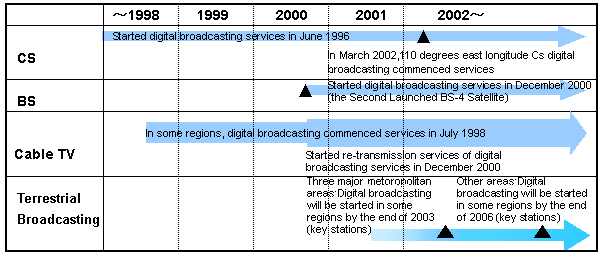
| 3) |
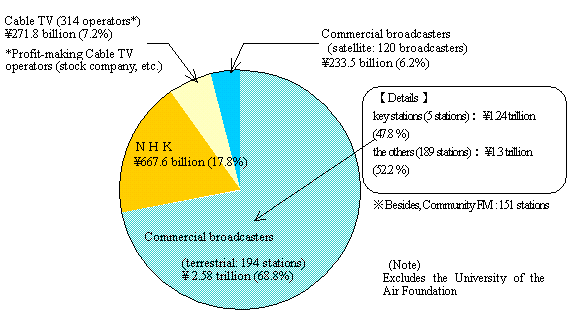
NHK ( Nippon Hoso Kyokai )
Established in 1950 to provide an abundant and high quality broadcast
programs to be received all over Japan, etc.
| |
Number of channels: |
2 TV channels; 4 radio channels [AM (2), FM (1) and short-wave
(1)] ; 3 channels of BS broadcasting (analog 3 channels, digital
3 channels (simulcasting) |
| |
Number of subscriptions: |
37.93 million households (includes 11.42) million households
receiving BS broadcasting)
[as the end of October 2002]
|
| |
Monthly amount of receiver's fee: |
color TV (terrestrial service only) contract ¥1,345 (account
transfer) satellite color TV (terrestrial & satellite services)
contract ¥2,290 (account transfer) |
|
| 4) |
The University of the Air Foundation
Established in 1981 to provide university-level education through broadcasting,
etc.
| |
Number of channels: |
2 channels of terrestrial broadcasting [TV, radio (FM)];
2 channels of communications satellite (CS) broadcasting (TV, radio)
[started broadcasting January 21, 1998]
|
|
| 5) |
Commercial broadcasting
i) Terrestrial broadcasting
| |
Number of broadcasters: |
127 TV broadcasters; 5 TV broadcasters specializing in TV multiplex
broadcasting; 253 radio broadcasters [AM (47), FM (49), community
FM (159), foreign-language FM (4), short-wave (1)]; 1 VHF broadcaster
specializing in teletext multiplex broadcasting (Vehicle Information
and Communication System: VICS) |
| |
|
[as of the end of November 2002] |
| Note: 47 AM broadcasters including 35
broadcasters also TV broadcasting |
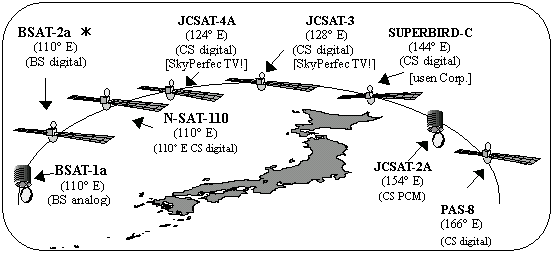
ii) Satellite broadcasting
|
a. Analog broadcasters via BS: |
2 broadcasters (1 TV broadcaster for 1 channel, 1 radio broadcaster
for 1 channel) |
| |
b. Digital broadcasters via BS: |
19 broadcasters (6 HDTV broadcasters for 6 channels, 7 SDTV broadcasters
for 19 channels, 10 radio broadcaster for 23 channels, 9 data broadcasters
for 9 channels) |
| |
c. Digital broadcasters via CS: |
107 broadcasters (104 TV broadcasters for 178 channels, 6 radio
broadcasters for 507 channels, 3 data broadcaster for 42 channels)
*exclusive of digital broadcasting via 110°E CS |
| |
d. Digital broadcasters via 110°E CS: |
18 broadcasters (1 HDTV broadcasters for 2 channels, 15 SDTV
broadcasters for 61 channels, 1 radio broadcaster for 20 channels,
8 data broadcasters for 10 channels)
(Service expected to start from april of 2002) |
| [as of December 1, 2002] |
|
| 6) |
Cable TV
| |
Number of operators: |
669 operators (those broadcasting original programs) |
| [as of the end of March 2002] |
|
| i) |
Legislative Action
| a. |
Revision of the Broadcast Law
| o |
Revision of the definition of TV broadcasting, etc. |
|
| b. |
Advanced Television Broadcasting Facility Development Promotion
Temporary Measures Law
| o |
Guaranteed Obligation by the Telecommunications Advancement
Organization of Japan (TAO) to support the development of
advanced television broadcasting facilities (combined with
tax incentives and interest-free loans or low interest loans). |
|
| c. |
Revision of the Radio Law
| o |
Financial assistance for the inevitable shift to other
analog channels, previous to the allotment of digital channels
for terrestrial television broadcasting. |
|
| d. |
Setting policies for permits for terrestrial digital television
broadcasting stations
| o |
Preparation of related ministerial ordinances for the start
of terrestrial digital television broadcasting (September
27, 2002) |
| o |
Receipt of applications for permits for terrestrial digital
television broadcasting |
|
|
(December 18, 2002-NHK plus 16 companies representing
the three major regional broadcast networks)
|
| ii) |
Establishment of Technical Standards
| May 1999: |
Establishment of standards for digital terrestrial TV broadcasting
by the Telecommunications Technology Council [OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency
Division Multiplex), SFN (Single Frequency Network), HDTV, multi-channel
broadcasting capability] |
| November 1999: |
Establishment of standards for digital terrestrial audio broadcasting
by the Telecommunications Technology Council [OFDM, CD-quality sound,
data broadcasting capability, improved mobile reception] |
| December 1999: |
Legislation of ministerial ordinances of standards for digital
terrestrial television broadcasting. |
| December 2000: |
Legislation of ministerial ordinances of standards for digital
terrestrial audio broadcasting. |
|
| iii) |
Establishment of Joint Study Committee Concerning Digital Terrestrial
Broadcasting
| June 1999: |
Announced schedule to allot digital channels for terrestrial TV
broadcasting. |
| September 1999: |
Establishment of the Joint Study Committee Concerning Digital
Terrestrial Broadcasting |
|
o Joint study to allot digital channels for terrestrial TV broadcasting
started among MPT, NHK and commercial broadcasters. |
| April 2000: |
The Joint Study Committee Concerning Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting
reported a draft of channel allotment plan for main broadcasting
stations, influenced households by the shift to other analog channels,
needed cost, etc. |
|
| iv) |
National Council for Promotion of Terrestrial Digital Broadcasting
| July 2001 |
Establishment of a National Council for the Promotion of Terrestrial
Digital Broadcasting by MPHPT,NHK and commercial broadcasters with
the aim of promoting a smooth transition from the present analog
broadcasting system to a digital broadcasting system and to further
the the development and spread of digital broadcasting. |
| August 2002 |
Announced the results of a study on the transition to other analog
channels, required outlay etc. |
|
o Required outlay : about
¥180 billion
o Number of households: affected
about 4.26million |
|
| |
i) |
Research and Development Facilities of Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting
System for Cooperative Usage (10 centers)
The TAO established 10 centers to offer facilities for local R&D basis
of contents and applications on new TV programs and provides technical
advice.
|
| |
ii) |
Association for Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting Development (10 associations)
Ten associations were organized by broadcasters, telecommunications service
providers, manufactures, educational organizations, distributors, local
governments, etc. for planning and carrying out R&D activities in
each area.
|
| |
iii) |
Conference on R&D Promotion for Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting
A promotion conference was established to support development activities
on nationwide network relay applications, etc. (established: September
1999)
|
| 1) |
Measures for viewer protection
| i) |
Enhancement of the "correction broadcasting system"
(Broadcast Law amended in 1995)
|
| ii) |
Strengthening of the "Consultative Organization on Broadcast
Program" (Broadcast Law amended in 1997) |
|
| 2) |
Enhancement of broadcasts for the aurally-
and visually-challenged
| i) |
Amendment of licensing provisions to promote broadcast programs
with captions and descriptions (Broadcast Law amended in 1997)
|
| ii) |
Establishment of subsidy system for production of captioned programs
(Started in fiscal 1993, revised in 1997)
|
| iii) |
Establishment of scheduling guideline for expansion of broadcasting
hour for captioned programs (Started in November 1997)
|
| iv) |
In view of digital era which the fusion of communication and broadcast,
and to promote captioned programs, MPHTP has been hold the "Study
group for research on next-generation broadcast programs with captions
and description" (from September 2001 to April 2002)
|
| v) |
In order to achieve the scheduling guideline for expansion of
broadcasting hour for captioned programs, MPHTP manages broadcasters's
plan for expansion of captioned programs. |
|
| 3) |
Establishment and management of the "Broadcast
and Human Rights/Other Related Rights Committee"(BRC)
| i) |
Established under the auspices of NHK and the National Association
of Commercial Broadcasters (NAB) as an entity to deal with complaints
concerning violations of rights.
|
| ii) |
Became functional as of June 1997 and announced the views and
recommendations of 10 cases adjudicated to the concerned broadcasters
as of December 10, 2002.
|
|
| 4) |
Investigation and research concerning policies
for viewers and listeners in the field of broadcasting
| i) |
Study Group for Research on Young People and Broadcasting (from
May 1998 to December 1998)
Proposals:
| o |
Improvement of broadcast programs for young people |
| o |
Improvement of media literacy |
| o |
Utilization of third-party agencies |
| o |
Improvement of provision of program information, etc. |
|
| ii) |
Working group on Young People and Broadcasting(from January 1999
to June 1999)
In response to the report of the above-mentioned study group, MPT,
NHK and NAB*– holds the working group, and each of them announced
the measure plan in regard to the each proposal item of the study
group.
*The National Association of Commercial Broadcasters in Japan
|
| iii) |
Study Group on Young People and Media Literacy in the field of
broadcasting(November 1999 to June 2000)
Announced the overall directivity with the improvement of media
literacy.
|
| iv) |
Development of the educational materials for media literacy and
its lending service(from August 2000)
|
|
| 5) |
Establishment and management of the Broadcasters Council for Youth Programs .
| i) |
Established in the Commission for better Broadcast Programs, as
an autonomous entity
|
| ii) |
To deal with the issues of young people and broadcasting, accepting
and discussing opinions and complaints about TV programs from viewers.
|
| iii) |
Became functional as of April 2000 .
For FY 2000, the Council accepted 2,605 opinions from 2,272 viewers.
For FY 2001, the Council accepted 2,439 opinions from 2,229 viewers.
|
|
| 1) |
Promotion of Production and Distribution of
Broadband-Contents
With regard to the production and distribution of broadband-content,
in order to realize the "e-Japan Strategy" at an early stage, MPHPT will
implement two measures, namely, i) measures for preparing an environment
for creating the content market by the private sector, and ii) measures
for complementing / strengthening content distribution. (Budget for fiscal
2002 (approximately 2.6 billion yen))
| i) |
"Development and verification of clearance system of copyrights"
In collaboration with other ministries, a market environment in
which copyrights of broadband content such as broadcast programs
are dealt between the right holders and the users will be developed
and verified.
|
| ii) |
"Development and implementation of technologies for supporting
broadband content distribution"
Checking administration of large-capacity digital video content
such as broadcast programs stably distributed over the high-speed
Internet will be provided for R&D of relevant technologies supporting
the distribution of broadband content.
|
| iii) |
" Development and verification of broadband content distribution
in the educational field"
Along with progress in deployment of broadband platforms in school,
in order to introduce ICT into education through making the most
of such platforms, systems tailored to educational use for ensuring
security and providing functions to authentication, billing, distribution
on networks shall be verified for promoting the distribution of
broadband content in classrooms. |
|
| 2) |
Enhancement and improvement in Broadcast Program
Production
| i) |
Assistance in Digitalization of Broadcast Program Production
Facilities, etc.:
Financial support for promotion of the digitalization of broadcast
program production facilities, etc. (supporting by tax system and
public spending (since FY 1998); by interest-free loans, low-interest
loans and debt guarantees (since FY 1999))
|
| ii) |
The R&D of an Advanced Contents Creation System in Okinawa
(Multimedia Model Studio):
Research and development of an advanced telecommunication system
to produce efficiently various broadcast programs in high definition
(Second supplementary budget for FY 1999 (900 million yen))
|
| iii) |
Study Group on Broadcast Program Production in the Broadband
Age:
For overall investigation of broadcast programming production with
a view to suggesting concrete measures for fairness and transparency,
it was set up in October 2002. This will function to increase the
social credibility of broadcasting in the age of broadband, and
work to consolidate and improve the production strengths for Japanese
broadcast programs, including their quality.
|
|
| 3) |
Measures for Archiving Broadcast Programs
| i) |
The R&D of a Digital Networking for Program Libraries:
Development of a system which make it possible to search, view and
listen to excellent programs archived in digital form through networks.
(Third supplementary budget for FY 1998 (2 billion yen))
|
| ii) |
The R&D of a Fundamental Technologies to Produce Broadcast
Programs utilizing of Large-scale Video Archives:
R&D of large-scale archiving technology for motion pictures,
data-compression technology and network-based video editing technology
(First supplementary budget for FY 1998 (3 billion yen)) |
|