Electronic Library System
The Electronic Library System enables users to obtain open digitized data from anywhere in the world by online access.
The Electronic Library System was developed on the basis of the following five concepts:
| Concept |
|---|
| Digital | Network | Interactive | Multimedia | Scalable |
With the various functions as shown below, the Electronic Library System supports a series of user's actions for searching and reading books.
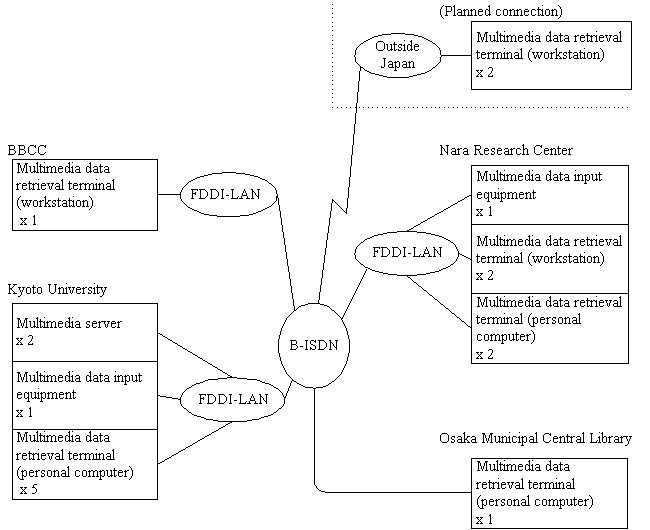
The Electronic Library System enables high-speed data transfer using a B-ISDN.
-
- Digital
- An electronic library has, not only text data but also sound, graphics, and motion video, in the form of digital data. Because all data is digitized, various kinds of data can be merged easily and a high level of retrieval and other processing can be done.
-
- Network
- When electronic libraries of this kind appear in many places and are linked to each other via a network, a huge virtual library is built on the network. It is a "world library" which crosses national borders regardless of the distances between actual electronic libraries.
-
- Interactive
- The Electronic Library System provides the latest functions as well as allowing books to be displayed on screen as if they were printed books. The system makes advances in retrieving books and papers. The system enables the user to display multiple books on a single screen and skip from one part describing an idea to a link describing the same idea within another book. It enables the user also to reference dictionaries and thesauruses simultaneously to check any unknown terms, attach notes and tags to various positions in a book, translate original text, and output text as voice data.
-
- Multimedia
- The user of the Electronic Library System can use data in different formats such as text, sound, graphics, and motion video. This multimedia data is more understandable than conventional books containing only text, diagrams, and tables.
-
- Scalable
- The Electronic Library System can be used to build an electronic library in various sizes according to the available hardware, software, and data resources. The electronic library can be as large as a national library and as small as a personal library.
-
- Bibliographic data retrieval
- Bibliographic data retrieval is a well-known function that is provided by existing library catalog systems and online data retrieval systems. The user can retrieve bibliographic data to find a book even if some of its title, author's name, publisher's name, publishing year, number of pages, and price are not known exactly.
The result of a retrieval can be displayed not only as a list of bibliographic data but also as a list of cover images.
-
- Hypertext retrieval
- Important data and concepts retained in the Electronic Library System are linked to groups of other data which can be located anywhere in the world.
This function enables the user to:
- Skip from one concept or term found in the current position of a book to another position where the same concept or term appears elsewhere in the same book or paper.
- Skip from one book or paper to another book or paper or to another book or paper stored in another library.
- Jump from a list of bibliographical data to an introduction of the author or the table of contents or a position in the text of a book.
- Jump from a book or paper directly to a quoted document.
- Check unknown meanings of terms found in a book.
Only a few examples can be given here, but many other types of linkage are available.
-
- Keyword retrieval
- Keyword retrieval enables the user to retrieve books and papers by inputting a keyword defied by the user. After full-text retrieval, the result is displayed as a list of books in which books are listed according to closest match with the user's request. Display items can include also an indication of the context in which the word appears.
-
- Retrieval using term hierarchy
- The user can retrieve data to find a book or paper by using a retrieval expression describing a hierarchical structure for books and paper in addition to the retrieval of its title, author's name, or publisher's name.
For example, to find a book whose title includes the term "Artificial intelligence," use the following retrieval expression:
BT (artificial intelligence)
Also, to find a book which discusses artificial intelligence from a philosophical viewpoint, use the following retrieval expression:
BT (artificial intelligence) * T (philosophy > artificial intelligence)
In comparison with the first retrieval expression, the second retrieval expression has an additional condition. The additional condition is that, in the hierarchy of the table of contents, a chapter or section whose title includes term "philosophy" must have a section or item whose title includes term "artificial intelligence."
As the result of retrieval, "Artificial Intelligence and Human Being" written by Nagao Makoto is found to be the only book that meets this condition. Also, translated words and synonyms can be used for retrieval.
-
- Simultaneous reference to multiple books
- While reading a book on the screen, the user can open new windows and easily read multiple books at the same time.
-
- Dictionaries
- Not only the dictionaries for the translation of words but also various other kinds of dictionaries are prepared. These dictionaries can be used for retrieval and to check the meanings of unknown words during reading. They can be used also to find the broader and narrower words or related terms for a specific term and reference the books or papers, at the same time, that include the words or terms.
-
- Notes and tags
- A reader sometimes writes down a part of the book in a notebook with comments or attaches tags at various positions in the book. The Electronic Library System enables the user to make these functions automatic. The user can attach tags and enter one line of notes for each tag. Obviously, the user can jump to such notes or tags by retrieving later.
-
- Translation
- The Electronic Library System can translate retrieved original text from Japanese to English, or vice versa.
-
- Speech output
- If the user is tired of reading, the user can listen to text output as speech in Japanese or English. This function can be applied, for example, to retrieve a Japanese book, translate its text, and output the English text as spoken English (or vice versa).
-
- Other reading support functions
- The Electronic Library System has many other support functions to facilitate reading. All of these functions cannot be explained here.
The following introduces some reading support functions that can interest the user:
-
- Jump function:
- The user can jump to the initial screen, table of contents, or index without having to move according to menus or operation history. Short-cut keys can be used to jump freely to a desired screen.
-
- Free setting of screen:
- The user can freely set the size of the screen for easy reading. The system automatically executes word-wrapping of text.
-
- Font switching:
- The user can change a Japanese font.
-
- Mail function:
- If the user finds an interesting description during reading, the user can mail it.
-
- Saving of user's environment:
- Various attributes set by each user can be inherited over sessions. Each user need not reset attributes for each session.