November 20, 2020 Draft of IMT-2020 Wireless Interface Recommendation Items by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
Concerning the fifth-generation mobile communications system (5G, IMT-2020*1) featuring ultra-high-speed, multiple simultaneous connections, and ultra-low latency, a draft of new recommendation items for wireless interfaces*2 was prepared at the 36th bis meeting of ITU-R SG 5 WP 5D held in November 2020 and submitted to the higher level meeting (SG 5).
1. Overview
The 5D Working Group (ITU-R SG 5 WP 5D) of the Fifth Research Committee of the Wireless Communication Division studied recommendation items for IMT-2020 (so-called 5G) as a next-generation mobile communications system expected to be realized around 2020. Its study started around 2014 after recommendation items were made for IMT-Advanced (so-called 4G) wireless interfaces.
The 36th bis meeting of ITU-R SG 5 WP 5D was held as an electronic conference from Tuesday, November 17 through Thursday, November 19, where work was done to create the new recommendation items for detailed IMT-2020 wireless interface specifications, and the draft was submitted to SG 5.
The three wireless interfaces specified below are recommended this time.
- 3GPP 5G–SRIT (3GPP*3 proposal for a combination of 5G NR and LTE)
- 3GPP 5G–RIT (3GPP*3 proposal for 5G NR alone)
- 5Gi (India’s TSDSI proposal)
2. Background and significance
As a process for developing IMT-2020, the outlook (vision) and definition of IMT-2020 have been examined since around 2014. Since 2016, requirements for candidate technologies and their evaluation criteria have been examined. Since 2018, consensus building has been made on technologies to evaluate and recommend candidate technologies. This time, the work to create the draft of the new recommendation items for WP 5D has been completed.
Concerning mobile communications systems, since IMT-2000 (so-called 3G) was recommended in 2000, the realization of globally unified technical specifications has become a major goal to provide international services according to market demands. Therefore, standardization organizations representing major countries and regions (hereafter referred to as the “SDOs”)*4 have taken the lead in accelerating the flow of jointly creating technical specifications, and 3GPP was established as one of the projects. SDOs participating in 3GPP have adopted 3GPP’s technical specifications as standards. Besides, technical specifications have been standardized among multiple SDOs.
The ITU enables a mechanism to refer to SDO standards in recommendation items that the ITU prepares. Also, ITU-affiliated agencies around the world provide a framework for participating in the process of recommendation approval. Therefore, standards recommended by the ITU are synonymous with standards that have been endorsed by countries around the world. It will be easier to accept them as more global standards.
Completing the draft of the new recommendation items at the ITU marks a milestone in this standardization process. For many developing countries that have not attended 3GPP or ITU meetings and have not yet launched 5G commercial services, the recommendation items will be important for their future adoption of 5G. They will also be significant for Japan in deploying 5G systems overseas.
Furthermore, release 15 of 3GPP technical specifications (i.e., a package consisting of technical specifications related to multiple technical items) was formulated in March 2019, and release 16 was formulated in July 2020. In response, in Japan, the Association of Radio Industries and Businesses approved these specifications as standards in July of last year and September of this year, and the Telecommunication Technology Committee approved these specifications as technical standards in June of last year and October of this year in Japan
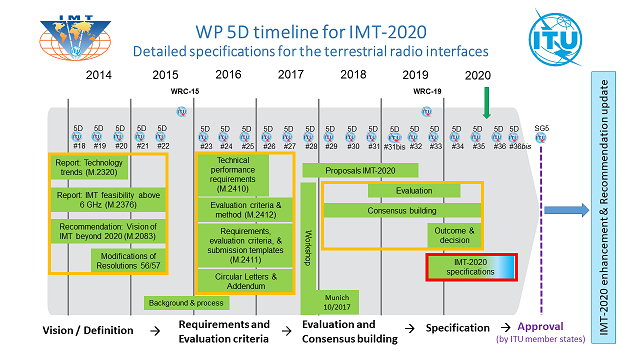
3. Future plans
The draft of new recommendation items will be confirmed and discussed at the 17th SG 5 meeting on Monday, November 23. The draft will be submitted to ITU member countries (a total of 193 countries) for postal voting for adoption and approval if there is no objection from the delegation of each country participating in the meeting.
If there is no objection from the member countries for two months from the start of the mail ballot, the draft of new recommendation items will be approved as ITU-R Recommendation (as a result, a recommendation symbol and number, e.g., M.2136, will be given). The result of the mail ballot will be revealed around the beginning of February 2021.
Considering that the introduction and dissemination of 5G will be further advanced and accelerated in response to formulating the ITU-R Recommendation, MIC will promote 5G in Japan and expand it overseas.
Note
- *1
IMT-2020: Short for International Mobile Telecommunications-2020, also referred to as 5G.
- *2
Wireless interfaces: Wireless communications methods that include defined communications, multiplexing, multiple access, and modulation modes.
In 3G, the following six are recommended as ITU-R Recommendation M.1457.- IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread (Proposal of Japan/Europe, W-CDMA)
- IMT-2000 CDMA Multi-Carrier (Proposal of the United States, CDMA2000)
- IMT-2000 CDMA TDD(Proposal of China and other countries, TD-CDMA and TD-SCDMA)
- IMT-2000 TDMA Single-Carrier (Proposal of the United States, EDGE)
- IMT-2000 FDMA/TDMA (Proposal of Europe, DECT)
- IMT-2000 OFDMA TDD WMAN (Proposal of the IEEE, Mobile WiMAX)
In 4G, the following two are recommended as ITU-R Recommendation M.2012.
- LTE-Advanced (Proposal of 3GPP)
- WirelessMAN-Advanced(Proposal of IEEE, WiMAX2)
SRIT: Short for Set of Radio Interface Technologies - *3
3GPP: Short for Third Generation Partnership Project. It is a project of an SDO jointly established by Japan, the United States, Europe, China, South Korea, and India in 1998 to examine and formulate specifications for mobile communications systems after 3G.
The technical specifications of 3GPP in the ITU-R Recommendation cover releases 15 and 16.
Japan’s proposal is included in 3GPP’s proposal technology. China and South Korea’s proposals are incorporated into the 3GPP proposal because the proposals are considered equivalent to the 3GPP proposal technology when formulating the draft recommendation items at the ITU.
Besides, the technology proposed by the TSDSI of India was partially incompatible with the technical specifications of 3GPP. Therefore, it will be reflected as a separate wireless interface in the ITU-R Recommendation. - *4
SDO: Short for Standards Development Organization. SDOs develop standards. Seven SDOs participates in 3GPP, i.e., ATIS (the United States), ETSI (Europe), CCSA (China), TSDSI (India), TTA (Korea), Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB), Information and Communication Technology Committee (TTC).
Contact
For further information about this press release, please fill in the inquiry form and submit it to MIC on the website
https://www.soumu.go.jp/common/english_opinions.html
International Policy Division, Global Strategy Bureau, MIC
TEL: +81 3 5253 5920
FAX: +81 3 5253 5924
