The Telecommunications Bureau is responsible for creating systems to ensure safe and secure information and communication in Japan by developing rules and an environment that form the basis of the use of information and communication services by all agents as follows.
The MIC is promoting the development of digital infrastructure based on the Digital Infrastructure Development Plan 2030(formulated in june2025)
Specifically, the MIC will promote infrastructure development in remote islands and other isolated regions in order to raise the national coverage rate for fiber optic broadband services for households to 99.9% by the end of FY2027. The MIC will also promote the development of regional terrestrial mobile phone stations with the aim of increasing both the population coverage rate for 5G and the road coverage rate for 5G, etc. to 99% by the end of FY2030. For the purpose of developing digital infrastructure, including optical fibers and 5G facilities, regional consultative meetings comprised of local governments and telecommunication business operators are held with the MIC acting as the secretariat. The MIC will continue those activities while listening to the voices of local communities.
In addition to promoting the development of data centers, the MIC will support the distributed location of landing stations and the development of branch lines of international undersea cables with a view to creating multitrack international undersea cables and promote the strengthening of Japan’s function as an international data distribution hub.
The MIC will also promote early domestic deployment non-terrestrial networks (NTNs), such as High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS) and satellite communication systems, which are useful for efficiently covering remote islands, offshore areas, and mountainous regions and securing redundancies for terrestrial networks.
In recent years, there have been significant changes in the Japanese telecommunication market, including the diffusion of mobile phones and broadband, and increased competition among groups by mobile phone service providers. Therefore, it is becoming more and more important to develop institutional systems to continue to secure a fair competitive environment in light of those changes. In order to facilitate the provision of a great variety of telecommunication services at low prices by telecommunication service providers, the MIC strives to develop a fair competitive environment in the telecommunication market.
While the advancement and diversification of telecommunication services has increased convenience and increased options for many users, there have been troubles caused by the digital divide between users and business operators and inappropriate solicitation activities. In order to develop an environment that prevents consumer troubles and enables consumers to use communication services safely, the MIC has repeatedly strengthened regulation by developing rules on the protection of consumers and is also monitoring business operators’ activities.
In recent years, concerns have grown among users over the acquisition and management of user information by business operators providing search, SNS and other platform services. Considering that, the amended Telecommunications Business Act, which provides for the development of rules of appropriate handling of user information of ICT services, was put into force in June 2023. Subsequently, regarding the Regulation on Handling of Specified User Information, which obligates large telecommunication business operators to submit internal rules concerning the handling of user information, publish policies for handling user information, and conduct selfevaluation of the status of the handling, business operators subject to the regulation were designated in December 2023 and the application of the regulation started in January 2024.
Furthermore, the MIC has institutionalized measures against electricity outage for telecommunication facilities and the communication line redundancy and has specified concrete countermeasures in the Guidelines for the Safety and Reliability of Information and Communication Networks. In this manner, the MIC is taking measures to ensure the continuation of communication services even in the event of a natural disaster.
Radio waves are common resources for the people that are widely used for services essential to their lives, such as mobile phone, wireless LAN, and commercial-use wireless communication. The MIC is implementing various measures, including appropriately allocating frequency bands, making international frequency adjustments, promoting R&D projects that contribute to effective use of radio waves, and developing an environment to adapt to new needs for the use of radio waves so that the benefits of radio waves can spread widely among the people and the Japanese society and economy can be revitalized by making effective use of the resources.
Under the abovementioned Infrastructure Development Plan for a Digital Garden City Nation, the MIC has been promoting the acceleration of development of 5G infrastructure with the aim of increasing the 5G population coverage rate to 97% by the end of FY2025 and to 99% by the end of FY2030. As a result, the MIC succeeded in moving forward the development of 5G infrastructure, with the 5G population coverage rate at the end of FY2023 coming to 98.1%, earlier than the target year.
In addition, the MIC is supporting infrastructure development under new development targets with respect to new technologies, such as high-frequency radio bands, namely the Sub-6 GHz and extra high frequency bands, and stand alone (SA) technology so that more and more users can enjoy the benefits of mobile phone services unique to 5G. In order to respond to rapid growth in mobile phone traffic in the future, the MIC is also promoting 5G, for example by having given assignment of a new radio band, such as the 4.9 GHz band, to mobile phone services.
Due to the expansion of use of drones in recent years, the need for aerial use of mobile phone networks and wireless LAN is growing. In light of those needs, in order to develop an environment for the use of drones, the MIC is considering such measures as increasing the scope of aerial use of mobile phones, expanding the frequency ranges for wireless LAN that are available for use by drones, and simplifying the licensing procedures under certain conditions.
To ensure the unimpeded use of radio waves, notably for important radio communications, such as police radio, fire defense radio, aeronautical and maritime radios and cellular phones, the MIC fulfills its responsibilities over the elimination of interferences and law enforcement on illegal radio stations on a routine basis. The MIC has also built database systems for radio stations, and conducts public awareness raising activities on facts and rules on the appropriate use of radio waves.
In addition, the MIC is working to provide an environment in which anyone can safely use radio waves with peace of mind, through the scientific analysis of the effect that radio has on the human body and the enactment of “radio wave protection guidelines” that provide guiding principles for the protection of people involved with radio waves, as well as regulations related to the radio waves escaping from various electric and electronic appliances.
Measures to deal with illegal and harmful information distributed on the Internet
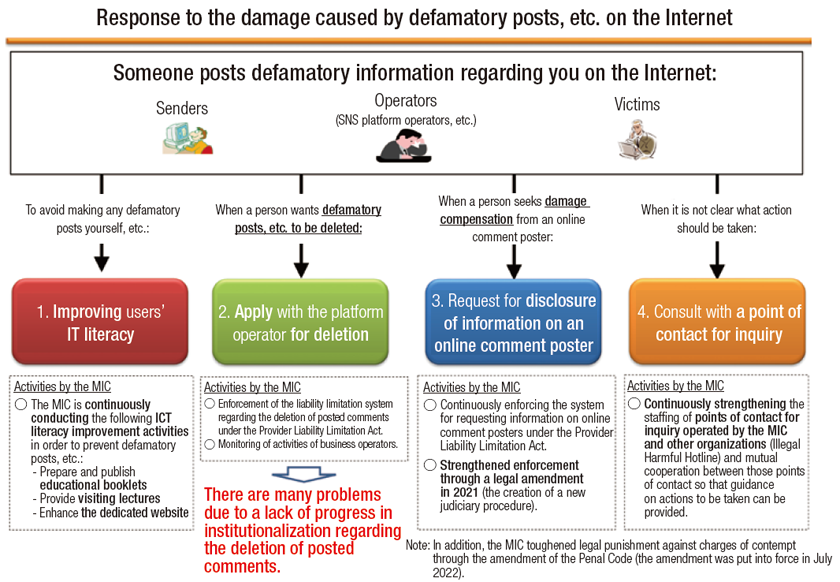
The arrival of the Internet has facilitated free and easy communications among people by enabling the dissemination of large volume information at high speed. Although this has brought significant benefits to our lives, it has also led to an increase in the distribution of illegal and harmful information, such as slander and defamatory one, which is a serious social problem.
In order to deal with illegal and harmful information distributed on the Internet, the MIC has adopted and implemented the following four key measures: (i) improving users’ ICT literacy, (ii) enhancing transparency over the post removal by platform operators, (iii) facilitating the disclosure of senders’ information, and (iv) strengthening response to inquiries. In particular, regarding (iii) facilitating the disclosure of senders’ information, the MIC has taken measures to strengthen enforcement, such as amending the Provider Liability Limitation Act in 2021 and creating new judiciary procedures concerning requests for disclosure of senders’ information.
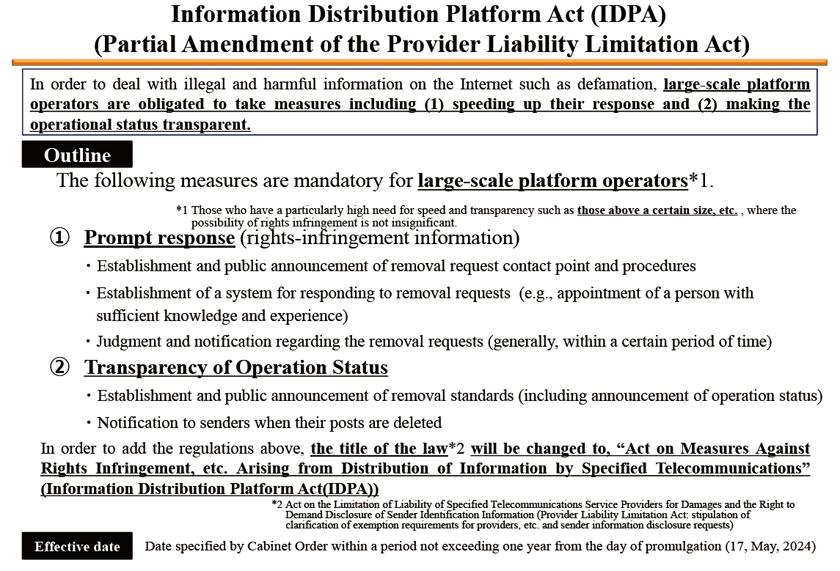
However, the volume of illegal and harmful information distributed on the Internet has still remained high. The number of inquiries received by Illegal Harmful Hotline (operated by the MIC) in FY2022 came to 5,745. In particular, there were many inquiries about post removal. In light of that, the MIC amended the Provider Liability Limitation Act in 2024 to obligate large platform operators to take measures including speeding up their response and making their operational status transparent. At the same time, the name of the act has been changed to the Act on Measures Against Rights Infringement, etc. Arising from Information Distribution by Specified Telecommunications (so-called “Information Distribution Platform Act”).
When dealing with illegal and harmful information distributed on the Internet, it is important to consider the balance between various rights and interests, including remedies for victims and senders’ freedom of expression. The MIC will implement further initiatives to develop an environment for a safe and secure Internet environment.
* Tasks related to measures to deal with illegal and harmful information were transferred to the Information and Communications Bureau in July 2024.